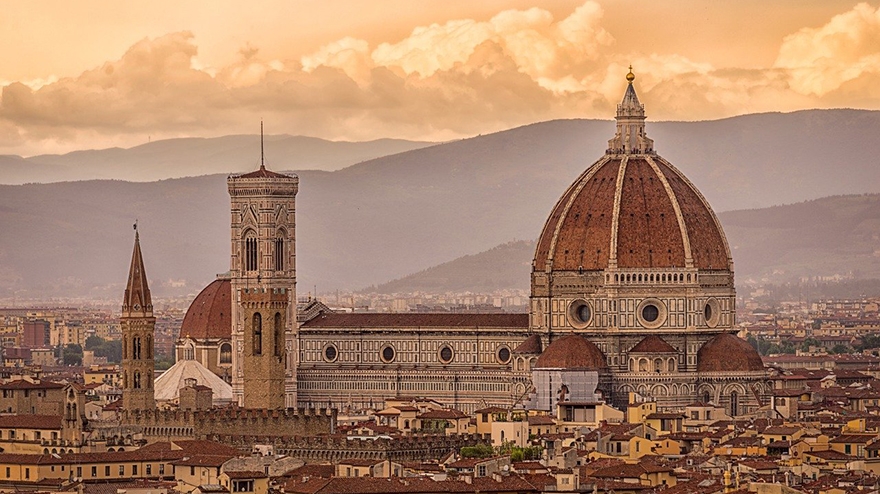

What is Renaissance Architecture?
The word ‘renaissance’ is a French word that means rebirth. Renaissance architecture is a style of architecture characterized by the rebirth and revival of the Classical Roman and Greek sense of design. It emerged in Florence and Italy between the 14th century and 16th century and spread across Europe.
Tudor architecture was the beginning of Renaissance architecture. Renaissance architecture was followed by Gothic architecture and Baroque architecture succeeded it.

Renaissance style of architecture emphasized on:
- Expression of humanism by designing based on human scale
- Symmetrical designs
- Simple mathematical proportions and geometrically perfect designs
- Hemispherical domes
- Classical columns
- Harmonious forms
Classical orders and other architectural features such as domes, columns, arches, pilasters, pediments, and entablatures are key elements of Renaissance buildings. Structures were designed in a way to connect with logic and emotions.
FILIPPO BRUNELLESCHI (1337-1446)
Filippo Brunelleschi is considered to be the pioneer of Renaissance architecture. He was also known as Pippo. Initially, he was trained as a goldsmith in Florence which was his native city. Soon his interests were turned towards architecture. He travelled to Rome to study the architecture of ancient buildings. He contributed to the development of cathedral architecture. He designed one of his greatest engineering accomplishments, the dome of Florence Cathedral. He developed a linear perspective technique in his artistic works.
He used the Classical orders Doric, Ionic and Corinthian orders in his buildings for the first time during this era. Though Brunelleschi designed simple buildings, he emphasized the system of proportions. Throughout the building, he used a unit of measurement in a way to create a sense of proportion and harmony. His works depict the elegance of architecture as well as mastery of engineering.
Florence Cathedral, Florence, Italy
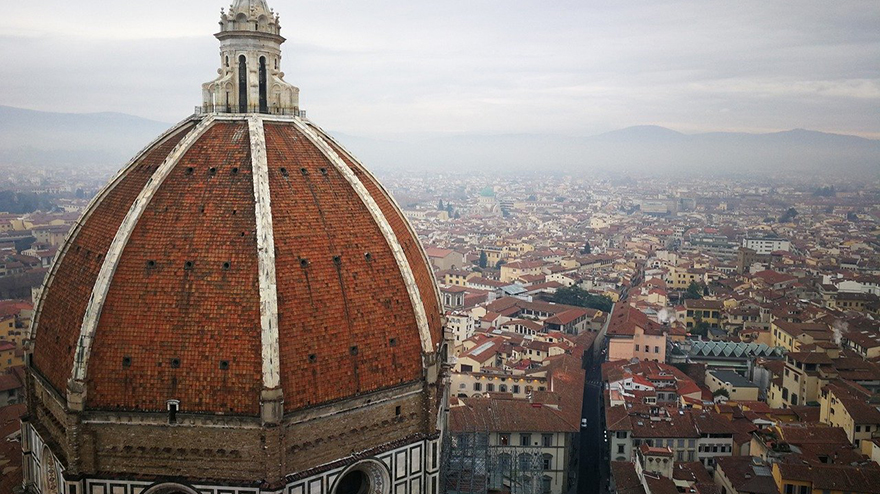

Filippo Brunelleschi designed the ribbed dome octagonal in form, one of the architectural and engineering masterpieces.
Ospedale Degli Innocenti, Florence, Italy
Ospedale Degli Innocenti is a children's hospital designed by Brunelleschi in Florence. He introduced the arcaded portico, a row of arches supported by columns decorated with few ornamental details. He transformed the shaft of columns from a polygonal to a circular shaft with a rich Corinthian capital.
LEON BATTISTA ALBERTI (1406-1472)
Although Leon Battista Alberti was a true Renaissance architect, he was also a musician, art theorist and humanist. He wrote some books inspired by Roman theorist Vitruvius, including one of the treatises on architecture by the name of De re Aedificatoria.
Alberti recreated the splendour of Classical times through his designs. He employed Classical Roman columns not only for decorative purposes but also as load-bearing supports. Alberti thought of architecture not only as a way of building structures but a means of creating meaning.
Tempio Malatestiano, Rimini, Italy
It is one of the most important churches in Italy. Alberti designed the façade inspired by Classical Roman architecture. Arcade with large arches and marble façade are significant features of the building.
Church of Sant’Ander, Mantua, Italy
It is designed based on Classical architecture. Here columns are not only serving as decorative features but as load-bearing structural elements.
ANDREA PALLADIO (1508-1580)
Andrea Palladio or Andrea di Pietro della Gondola was an Italian architect born in Padua, Italy. Palladio designed various villas, palaces and churches mostly in Venice as well as neighboring areas. He designed his buildings on Classical Roman principles without rich embellishments. His Palladian style became so famous that it went across Europe. Christopher Wren was highly impressed by his style of architecture.
He also wrote a few books on architecture such as The Antiquities of Rome and Palladio’s Four Books on Architecture. Palladio focused on residential architecture due to the increasing need for villas. His villas took influence from Roman country villas with central planning. One of his famous villas is Villa Rotonda, where the architect emphasized the concepts of symmetry, clarity and axiality.
Villa Rotonda, Vicenza, Italy
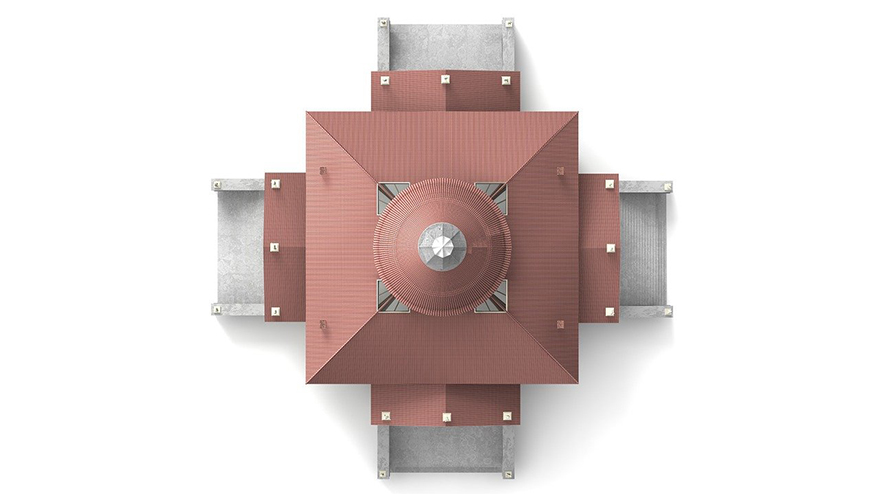
Palladio designed a simple villa influenced by the Pantheon, Rome. It has a square structure with symmetry on all four facades. Each façade has a portico leading to the central circular chamber topped with a dome.
Villa Emo, Fanzolo di Vedelago, Italy
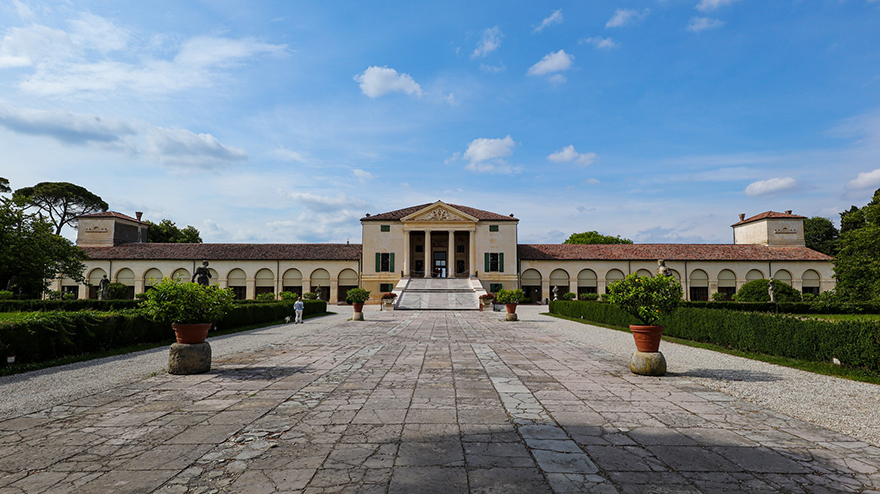

Palladio designed this villa in Fanzolo di Vedelago on Classical architecture. The central entrance exhibits four columns in the style of a Greek building.










