
Types of Wood Used in Architecture and Construction
Wood has been in use since ancient times for producing fuel, making paper, manufacturing tools, weapons, furnishings, and artworks, and also as a building material to construct houses. Wood was largely used for making furniture and as a construction material in timber architecture dating back some thousands of years. The Neolithic long house is evidence of the use of wooden construction in old age. This timber structure was rectangular and was largely built of wood by ancient farmers in Europe around 5000 to 6000 BC.
The age of the wood can be determined using the methods of dendrochronology and radiocarbon dating. Dendrochronology, also known as tree-ring dating, finds out the accurate year of tree rings or growth rings when they were developed to identify the precise age of a tree. Radiocarbon dating, also known as carbon dating and carbon-14 dating, finds out the approximate age of a tree.
As it is an organic natural material, wood has been of immense significance as a source of sustainable and renewable energy. In modern times, wood has been used with other materials such as steel and bronze in the wood architecture and construction industry in Pakistan as well as throughout the world.
Wood

Wood is a hard fibrous and porous substance present in the branches, stems, and roots of trees and shrubs. It is a natural composite of fibres embedded in lignin. Lignin is a substance that forms the walls of plant cells making them hard primarily in the bark. Fibers resist tension and lignin is strong in compression. Wood is an organic substance generally composed of xylem that forms a large part of the branches, stems, and roots under the bark. The xylem is a transport tissue whose key function is to transport nutrients and water to stems and leaves from the roots. Xylem also physically supports the plant.
Branches at a lower level of the tree drop off sometimes. The base of such a branch gets enclosed by the wood growth to develop a lump, subsequently forming a knot. Knots reduce the structural strength of wood but these imperfections in wood have an aesthetic value in the residential and commercial sectors.
Types of Wood
In the construction industry, a felled or cut down tree is known as lumber whereas the word timber is used for sawn wooden planks. There are many different types of wood available in the market that are used in the wood architecture and construction industry and wood architecture in Pakistan.
Hard Wood
Wood yielded from dicotyledonous trees is known as hardwood. A dicotyledonous tree is one of the two types of flowering plants (angiosperms), with two cotyledons and usually having broad leaves. Such trees are also called dicotyledons or dicots. The developing seed in a dicot has two embryonic leaves in it. They are generally found in Earth’s temperate zone and tropical zone (torrid zone). Temperate forests lie in a temperate zone, a region between the tropics and frigid zones. Tropical forests lie in a tropical zone that is the region surrounding the equator between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.

Trees in temperate and boreal regions are often deciduous and shed their leaves during the autumn season. On the other hand, they are largely evergreen in tropical and subtropical zones. Black ironwood is one of the hardest woods with high density. Hardwoods may not always be harder than softwoods. Balsa is a hardwood but is softer as compared to any common softwood. As it is less dense and lighter, it is used in model making.
Soft Wood
Wood produced from gymnosperms or acrogymnospermae is known as softwood. Gymnosperms are plants that yield seeds. They include cycads and conifers such as pine, spruce, and others.
Softwoods may not always be softer than hardwoods. Douglas fir, yew, and longleaf pine are softwoods but are harder as compared to various hardwoods.
Softwoods are mostly used in the construction field such as in the manufacturing of doors, door frames, architraves, panels, flooring, roofing, decking, exterior cladding, joinery, furniture, railings, stair treads, and others.
Wood in Construction
In Medieval times, oak wood was used in construction for making floors, walls, beams, and doors. Douglas fir, poplar, and pine are used to manufacture solid wood doors these days. Woodwork plays an influential role in various sectors of construction. Timber framing has a significant value in the construction of dwellings in various countries throughout the world. Wood has also been used for shuttering purposes in reinforced concrete structures to make formwork so wet concrete mixture can be poured in to take a specific shape.

Hardwood is mostly used for making planks made of solid wood for flooring. As wood loses and absorbs moisture from its surroundings, due to this factor dimensions of the wooden planks cannot be increased to a certain size. Flooring made of solid hardwood is generally less expensive than engineered wood flooring. Whenever there occurs some scratch or other damage on solid wood, it is sanded and given a finish to completely erase the defect.
Many different types of wood used in construction are Ashwood, Walnut, Teak, Deodar, Chir Pine, Oak, Hemlock, (local name: Shekran), Cherry, Acacia, Mahogany, Sheesham (local name: Tali), and many others.
Wood in Furniture & Tools
Wood has often been used for making furniture such as beds, sofas, chairs, tables, and cabinets. It is also employed in making utensils, chopsticks, spoons, toothpicks, tool handles, lead pencils, etc.
Ikea is a big brand in the world making good quality affordable furniture using different kinds of hardwood and softwood in various forms such as solid wood, laminated boards, MDF, and others.
Wood in Sports
Wood has been used to make various kinds of sporting goods as white willow wood is primarily used to make cricket bats and baseball bats are made up of hickory or ash wood. Ice hockey sticks were made of willow wood. Other sports equipment such as archery bows, skis, and golf clubs also known as the woods were also made from wooden materials. Moreover, parquet flooring has been used for NBA courts (National Basketball Association).
Types of Engineered Wood
Engineered wood is a composite material that is manufactured by fixing wood fibres, particles, wood strands or flakes, veneers, or wooden boards using adhesives or other means of binding the materials together to make a strong unit.
Engineered wood plays an important part in the growth of the construction industry today. Products made of engineered wood are employed in residential as well as commercial projects for structural stability and visual importance.
Where wood is not suitable to be used for construction, it is crushed mechanically or chemically into chips, fibres, or wood cellulose. This crush is then used to make other wooden materials like engineered wood.

There are different types of engineered wood products available in the market. They include laminated veneer lumber (LVL) usually used for headers and beams, containing many thin layers of wood fixed together by adhesives.
Plywood
Plywood is also an engineered wood product made with several plies or thin wooden layers assembled with glue having plies placed with their wooden grains perpendicular to those of the layer adjacent. Plies are thinly sliced wood layers or wood veneers. These plies are assembled in a way so that the grains of adjacent layers are at 90 degrees with each other and then are glued together.
Chipboard - Particleboard
Chipboard is a type of engineered wood made up of wood chips mixed with a suitable resin or some other synthetic binding substance, pressed together and extruded to formulate a board. Chipboards are lighter in weight but higher in density than solid wood. They can be veneered to give them an aesthetic surface finish. They absorb moisture so their usage is avoided in wet areas. Due to their low strength, their cost is lower as compared to that of MDF, plywood, and solid wood. Chipboard is also known as particle board.
Laminated Chipboard
Laminated chipboards are ordinary chipboards but they are covered with a thin PVC laminated sheet or wood veneer for a surface finish. They are usually used indoors for making cabinets and wardrobes.
Oriented Strand Board
Oriented strand board is another engineered wood product made of layers of wood flakes or wood strands placed in particular orientations and compressed together with suitable adhesives to make panels. It is also known as a wafer board or flakeboard.
It is generally used for load-bearing activities in the construction industry. It is commonly used for exterior wall cladding, flooring, and decking on roofs. It is also used to manufacture furniture.
Medium Density Fibreboard - MDF
Medium-density fibreboard is a type of engineered wood formed by breaking down residues or wooden leftovers of softwood or hardwood and converting them into wood fibres usually by using a defibrillator, mixing them with some wax and a suitable resin or other binders, and placing them under high pressure and temperature to shape them into boards. A defibrator is a pulping refiner and a thermo mechanical equipment where the raw wood pulp or fibrous material from wood such as woodchips is broken down in heat by stationary and rotating discs for grinding and refining the substance.

It is commonly known as MDF in the local market using the abbreviations of Medium-density fibreboard. MDF is denser and stronger than plywood chipboard or particleboard. It has a density between 31 pounds per cubic foot and 50 MDF pounds per cubic foot. MDF panels can be painted, glued, veneered, and laminated. Although MDF panels are moisture-resistant, they are mostly used indoors. They are usually employed in laminate floors, engineered floors, kitchen cabinets, furniture, wall panels, shelves, storage units, skirting, decorative edges, doors, etc. There are various other types of MDF available such as ultralight MDF, fire retardant MDF, and moisture-resistant MDF. They are usually available in size of 4’ wide by 8’ high with half-inch thickness.
High-Density Fibreboard - HDF
High-density fibreboard is a type of engineered wood manufactured similarly to MDF but with much higher density. It is denser and harder than medium-density fibreboard. Its density is between 50 pounds per cubic foot and 65 pounds per cubic foot. It is also known as a hardboard. It is a suitable material for laminate flooring and engineered flooring.
Low-Density Fibreboard - LDF
Low-density fibreboard is a type of engineered wood manufactured similarly to MDF but with a much lower density. It is less dense than medium-density fibreboard. Its density is between 28 pounds per cubic foot and 31 pounds per cubic foot.
They are usually used in dry applications such as interior designing and thermal insulation purposes.
Types of Wood Veneers
A wood veneer is a thin layer of solid wood that is sliced from the tree trunk. The thickness of the wood veneer is generally 3 mm, i.e., 1/8 inch. They are glued on various kinds of engineered wood panels to give them a smooth and beautiful finish showing natural wood grains and color.

There are a few types of wood veneers depending on the way they are peeled or sliced off the wood log.
Rotary Cut Veneer – Flat Sawing Veneer
A rotary cut veneer is obtained by slicing the wood log using a sharp blade or knife along the circumference of the tree trunk more like unwinding a paper towel roll. This method produces a whole continuous sheet with a variegated wood grains pattern.
Plain Slicing Veneer
Plain slicing veneer is obtained by slicing the whole wood log with a sharp blade along one direction only, parallel to each other more like cutting linear potato fries. This method produces smaller slices of veneers with repeated grain patterns.
Rift Sawing Veneer
Rift sawing veneer is obtained by cutting thin slices in a way so that the face is neither perpendicular nor parallel but makes an angle of 30 degrees to 60 degrees to the growth rings of the trunk. This method produces grains with tightly packed straight lines.
Quarter Sawing Veneer
Quarter Sawing Veneer is obtained by slicing thin layers by cutting the log in a way so that the face is perpendicular to the growth rings along radial geometry making angles between 45 degrees to 90 degrees. This method also produces grains with tightly packed straight lines.
Types of Wood Joinery Used in Woodworking
Different pieces of wood are joined together using various methods such as interlocking, nails, screws, and glue to establish stability. There are different types of joints used by carpenters in the woodworking industry.
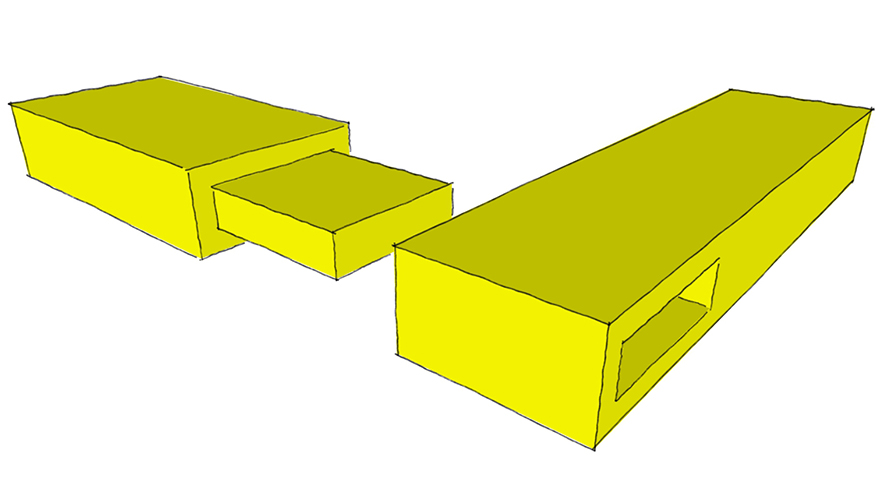
Dado Joint
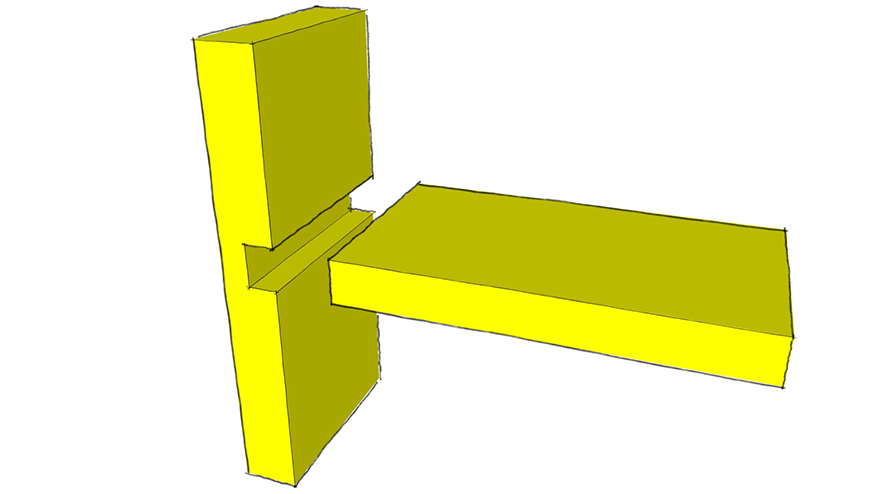
Basic Butt Joint
A basic butt joint is a joint where one piece of wood is placed with the other piece usually at a right angle. This is the simplest form of a joint in wood joinery.
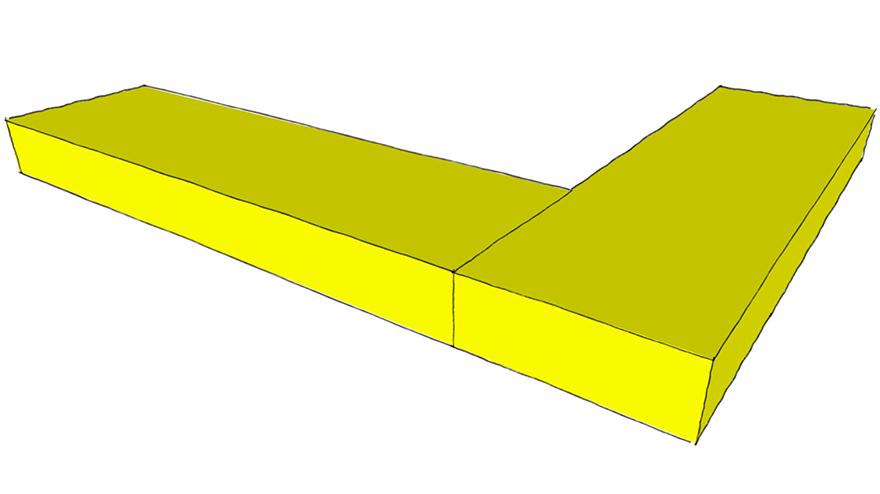
Mitered Butt Joint
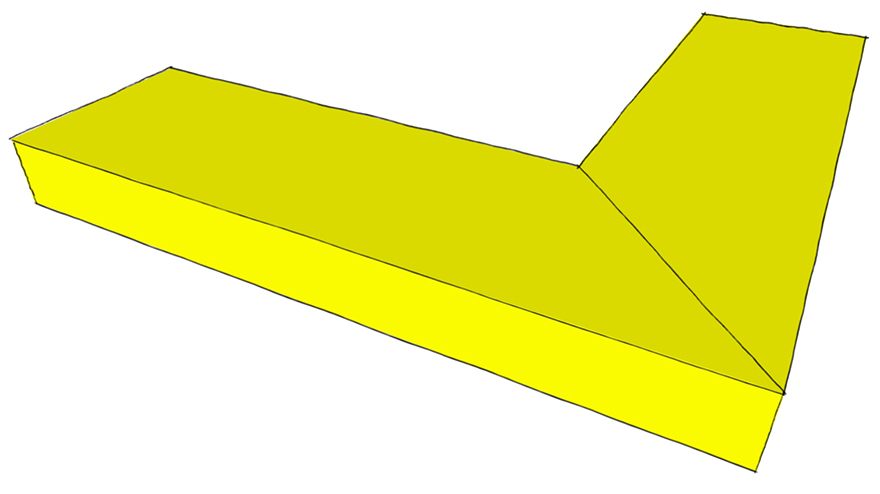
Half Lap Joint
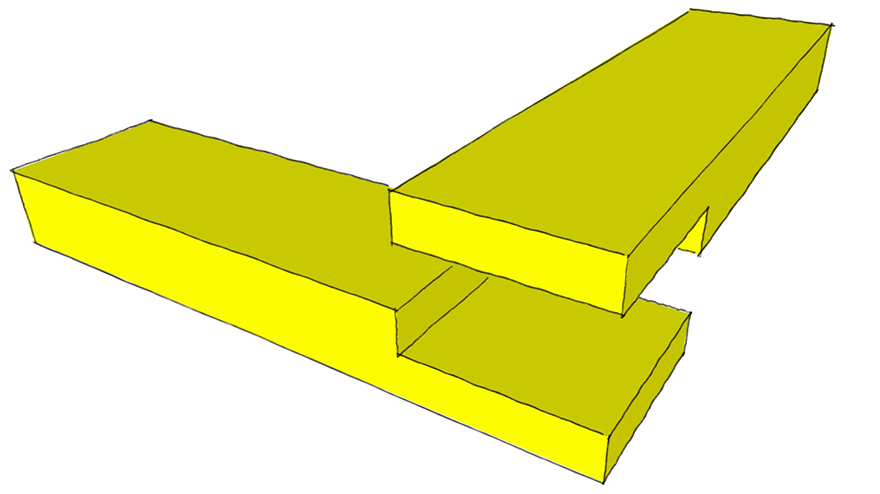
Mitered Half Lap Joint
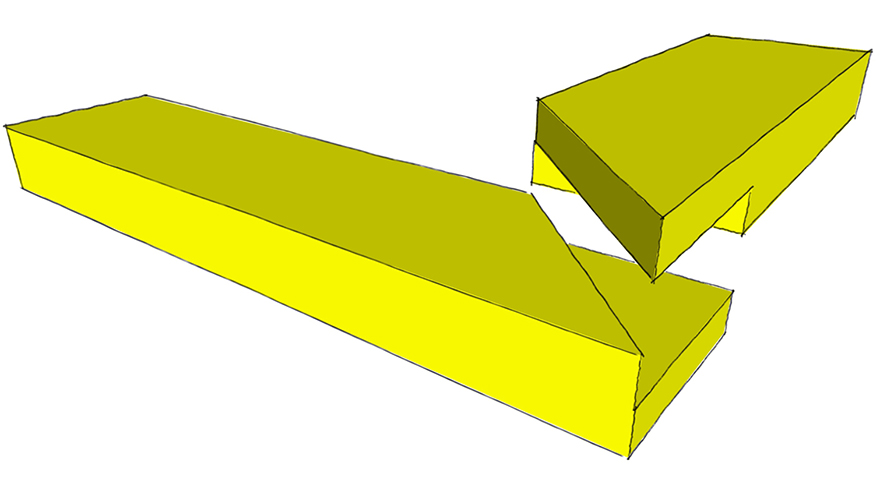
Cross Lap Joint
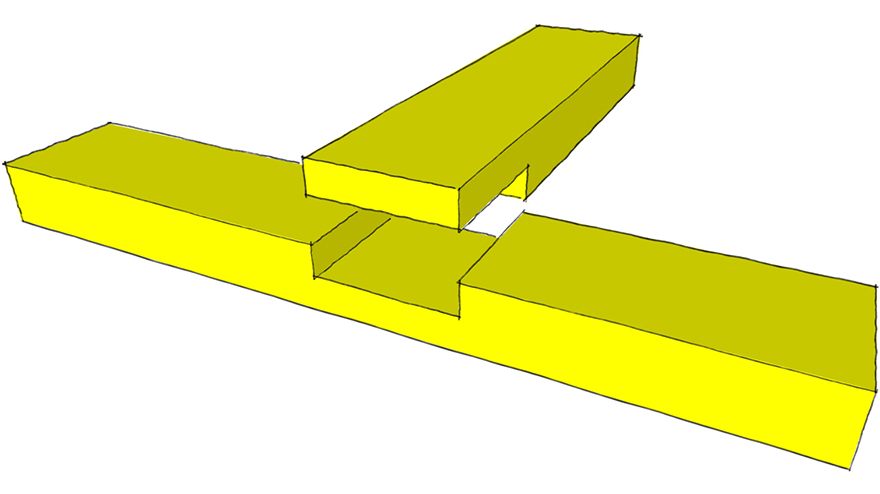
Dovetail Crossed Lap
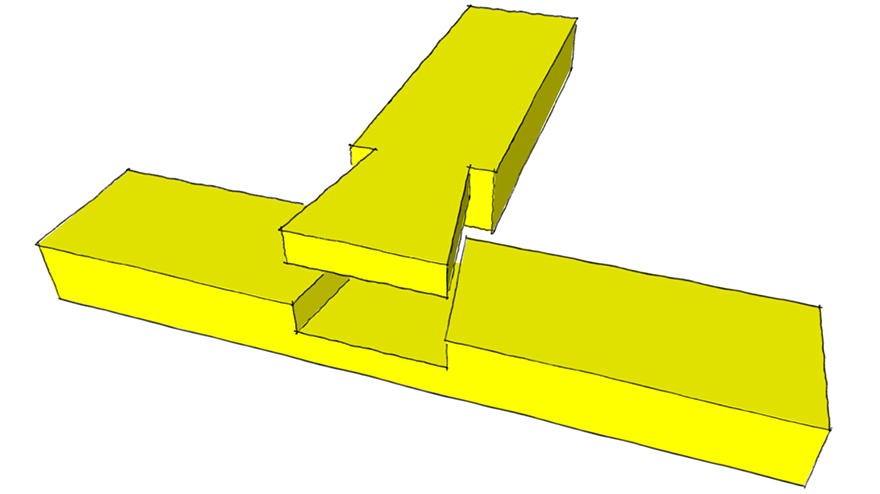
Half Blind Dovetail Joint
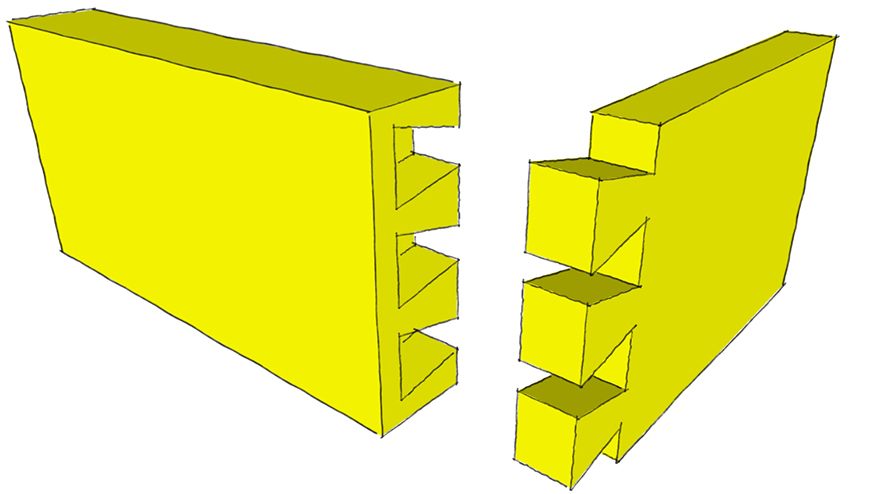
Tongue and Groove Joint
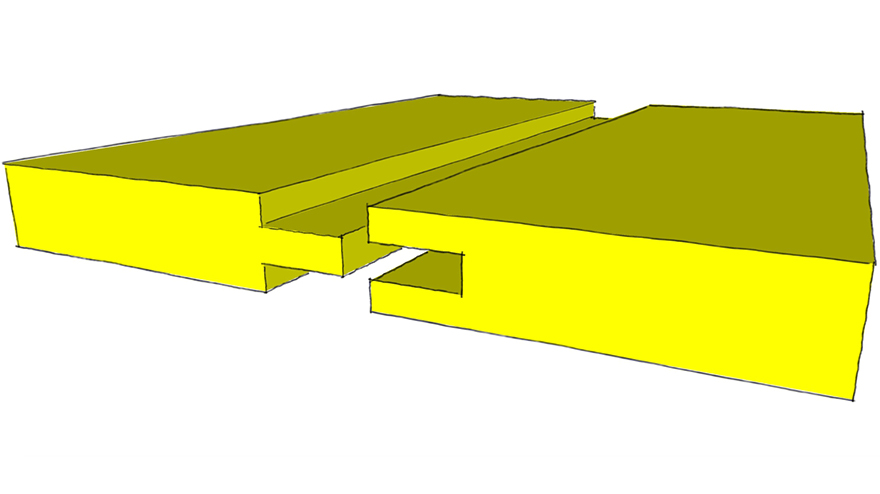
Rabbet Joint
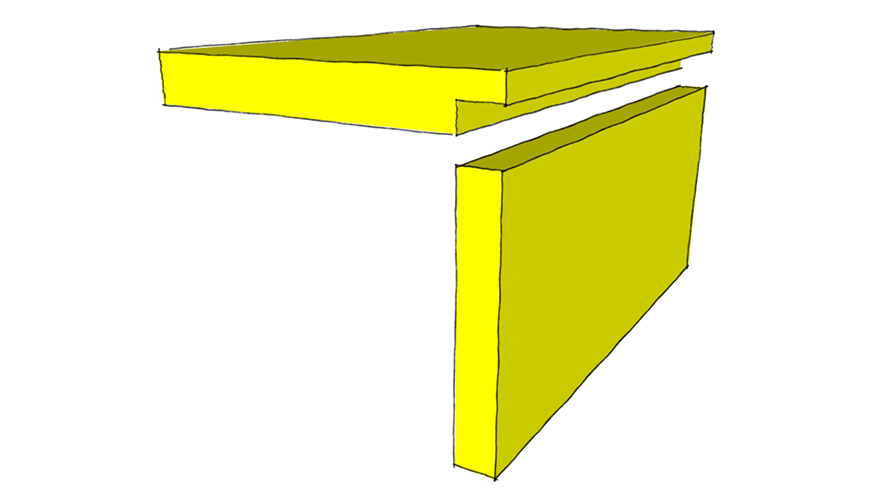
Pocket Joint
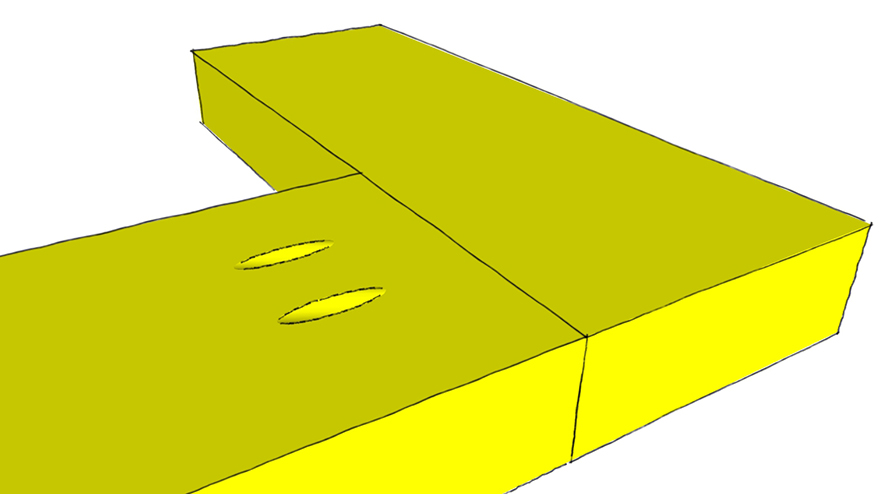
Biscuit Joint
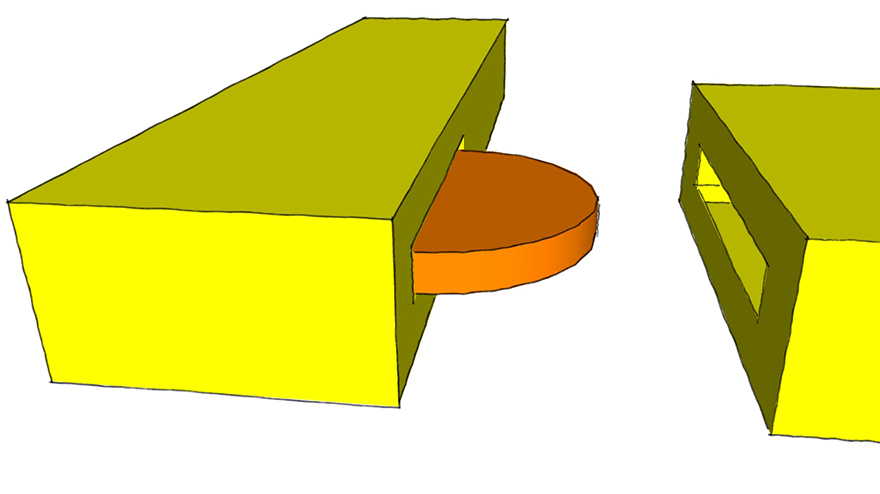
Mortise and Tenon Joint
Best Wood Types to Use in Pakistan
For different styles of furniture, whether it is minimal furniture or contemporary design, wood plays an influential part in the ambience of the overall space. Wood has other functions apart from being used in furniture such as floors, walls, and ceilings.
Here are some of the best wood available in the Pakistan woodworking market.
Ash Wood
Ash is a pale and light-coloured hardwood with a light brown or beige tone. It is strong and light in weight. It is used in making curved furniture due to being flexible.
Deodar
Deodar is a hardwood and is commonly used in construction in Pakistan. It is repellant to rot, germs, and bacteria and is termite resistant. It is a strong and very durable wood. It is also known as Diyar.
Mahogany
Mahogany is a hardwood with a deep reddish to reddish brown tone. It is mostly used for manufacturing furniture such as beds, sofas, tables, and consoles.
Sheesham or Shisham
Sheesham is a hardwood with a darker brown to golden brown tone. It is used in the manufacture of furniture. It is also known as Tali or Tahli in Pakistan.
Teak
Teak is a hardwood with a golden brown colour. It is resistant to moisture. It is used to make furniture, cabinets, window frames, and door fittings.
Walnut

Walnut is a hardwood and is resistant to moisture. It is used to make furniture and decorative elements for ceilings and walls.
Chir Pine
Chir Pine is a softwood with a pale tone. It is used in making furniture, door panels, carvings, and other decorative artistic patterns.
Hemlock
Hemlock is a softwood. It is mainly used to manufacture furniture, planks, windows, and doors. It is not a good idea to use it for flooring as it is absorbent to moisture. It is also known as Shekran in Pakistan.
Fir
Fir is a softwood with a lighter tone. It is used to make doors and window panels in timber architecture.











COMMENTS
Wow great